In today’s fast-paced business world, efficiency and quality are more crucial than ever. To excel in this environment, organizations need robust methodologies that not only streamline processes but also drive continuous improvement. Lean Six Sigma is one such methodology that has proven time and again to be a game-changer. In this blog, we will explore the key principles, methodologies, and benefits of Lean Six Sigma.
Chapter 1: Understanding Lean Six Sigma
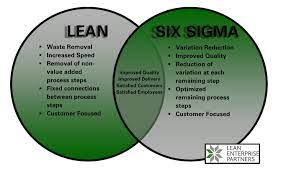
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology that combines the principles of Lean and Six Sigma to improve process efficiency and quality. Lean focuses on eliminating waste, while Six Sigma aims to reduce defects and variations. Together, they create a powerful framework for process improvement.
Key Principles of Lean Six Sigma
- Customer Focus: Identifying and meeting customer requirements is paramount.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Using data and statistical analysis to drive improvement.
- Process Mapping: Visualizing and understanding current processes.
- Continuous Improvement: Striving for incremental, ongoing enhancements.
Chapter 2: Lean Six Sigma Methodology
DMAIC vs. DMADV
- DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) is used for improving existing processes.
- DMADV (Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, Verify) is used for creating new processes or products.
Tools and Techniques
Lean Six Sigma offers a wide range of tools, including Pareto charts, Fishbone diagrams, Value Stream Mapping, and Statistical Process Control, to help in problem-solving and decision-making.
Chapter 3: Benefits of Lean Six Sigma
Enhanced Efficiency
Lean Six Sigma identifies and eliminates inefficiencies, reducing lead times and improving resource utilization.
Improved Quality
By reducing defects and variations, Lean Six Sigma ensures products and services meet or exceed customer expectations.
Cost Reduction
Eliminating waste and optimizing processes can lead to significant cost savings.
Competitive Advantage
Organizations that embrace Lean Six Sigma often outperform their competitors, gaining a distinct market advantage.
Chapter 4: Lean Six Sigma Success Stories
Toyota
Toyota is renowned for its successful implementation of Lean principles, which have revolutionized the automotive industry.
General Electric (GE)
GE saved billions of dollars by integrating Lean Six Sigma into its operations, proving its effectiveness on a large scale.
Amazon
Amazon uses Lean principles to optimize its supply chain, ensuring efficient product delivery and customer satisfaction.
Chapter 5: Getting Started with Lean Six Sigma
Training and Certification
Consider investing in Lean Six Sigma training and certification for your team to build the required skills.
Project Selection
Identify projects with a significant impact on your organization’s goals and customer satisfaction.
Cultivating a Lean Culture
Embed Lean Six Sigma principles into your organization’s culture, promoting a mindset of continuous improvement.